Institutional Governance
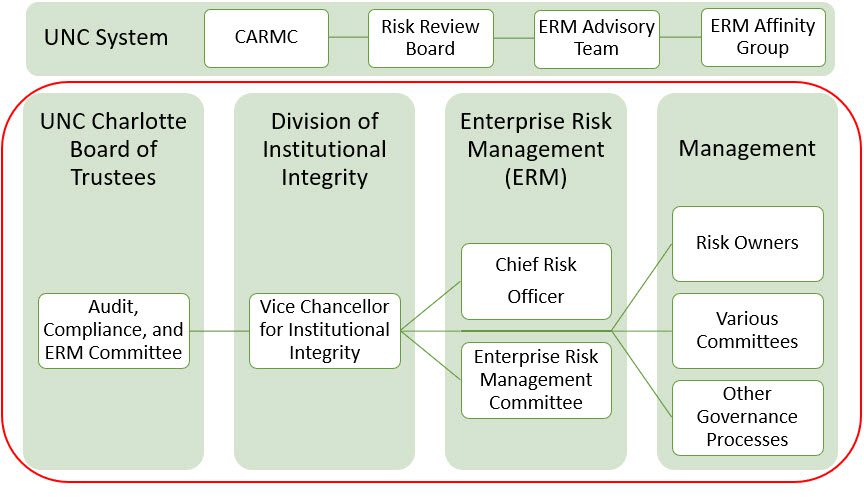
Audit, Compliance and Enterprise Risk Management (ACERM) Committee
Per the ACERM Bylaws Section 3 (d) (ii) (U):
- Review any and all issues related to enterprise risk management that are brought to the attention of the Board, and
- To receive such reports as the Committee requests on issues related to enterprise risk management.
Every board has an oversight role, helping to support the creation of value in an entity and prevent its decline. Traditionally, ERM has played a strong supporting role at the board level. Now, boards are increasingly expected to provide oversight of ERM.1
Division of Institutional Integrity (DII) – Legal, Title IX, Audit, Compliance, and ERM
After a thorough evaluation of audit, governance, risk and compliance best practices, in 2016 the Chief of Staff recommended, and the Chancellor approved, the formation of the DII. The Comprehensive Division Reorganization report specifically stated:
- The ERM function be proximate to, and have direct access to, the top of the university;
- Placing ERM near other important risk functions to promote a risk-conscious culture;
- Some interviewees noted that ERM simply would not be possible without access to data that is not commonly centralized, so placing ERM alongside units that can inform and enhance ERM is important; and
- Mark Beasley and Bonnie Hancock at the NC State ERM Initiative could not overstate the importance of linking ERM development to strategy.
Chief Risk Officer (CRO)
- Manages the design and operation of ERM Program.
- Responsible for developing and maintaining foundational risk register and objectives needing risk assessment.
- Coordinates and Chairs activity of the ERM Committee (ERMC).
- Facilitates development of seven part risk assessment process for prioritized risks and objectives.
- Facilitates remediation of excessive residual risk.
- Provides regular reporting to the ERMC, Chancellor, ACERM, and UNC System Office on ERM Program operations.
ERM Committee (ERMC)
Cross divisional governance body with primary responsibility over the University’s effectiveness at managing key strategic and emerging risks.
- Assures completeness of risk register and key strategic objectives that can most benefit from risk intelligence.
- Prioritizes the evaluation of specific risks and objectives to help optimize residual risk and the achievement of objectives.
- Provides oversight and accountability on acceptable levels of residual risk.
- Providing advocacy (functional, political, financial, etc.) for improved mitigation efforts.
Management
While the Chief Risk Officer has responsibility for the ERM Program, ultimately management holds overall responsibility for managing risk.2 Integrating risk management into an organization is a dynamic and iterative process, and should be customized to the organization’s needs and culture. Risk management should be a part of, and not separate from, the organizational purpose, governance, leadership and commitment, strategy, objectives and operations.3
Risk Owners
Risk owners are specific subject matter experts assigned direct responsibility for monitoring and managing residual risk within acceptable levels. Risk is managed in every part of the organization’s structure.4
Various Committees
The University employs many committees to oversee cross divisional objectives and risks. Some committees are formally charged by the Chancellor while many others are less formally charged. In either instance, these various committees play significant roles in risk governance and at times are overtly charged with risk ownership.
Other Governance Processes
As the management of risk and the achievement of complex objectives is a pervasive effort in the organization, other governance processes play a significant role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risk. Departments such as Internal Audit, Compliance, Risk Management, Safety & Security, Legal Affairs, HR, IT, Title IX, Assessment & Accreditation and many others contribute to a risk informed culture and achievement acceptable levels of residual risk.
Footnotes:
1 2017 COSO ERM Executive Summary, Page 2
2 2017 COSO ERM Executive Summary, Page 1
3 ISO 31000 5.3
4 ISO 31000 5.3